Quick Start
This guide walks you through building your first flow - a text transformation API that receives text via HTTP and returns it in uppercase.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”You need access to a Spacelift Flows organization. Organization admins can invite users. If you’re the org admin, you can create flows immediately.
Step 1: Access Your Project
Section titled “Step 1: Access Your Project”Go to the Projects view and select your Personal Sandbox project. Every user gets a sandbox for testing flows.
Step 2: Creating a New Flow
Section titled “Step 2: Creating a New Flow”Click ’+ New flow’ in the top right corner. Give your flow a descriptive name like “Text Transform API”.
Step 3: Understand the Interface
Section titled “Step 3: Understand the Interface”You’re now in the flow editor:
- Left sidebar: Block types you can add (Core blocks and App blocks)
- Right sidebar: Configuration for selected blocks
- Center canvas: Where you place and connect blocks
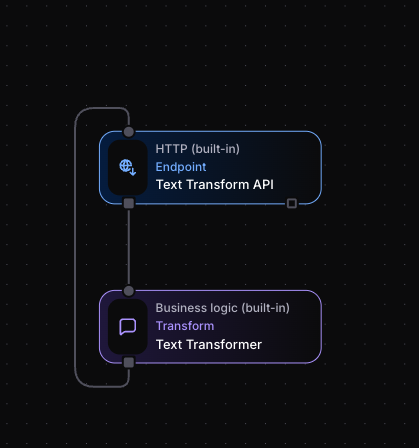
Step 4: Add Blocks
Section titled “Step 4: Add Blocks”Create two blocks:
HTTP Endpoint Block:
- From Core Blocks, click “HTTP Endpoint”
- Place it on the canvas
- This receives incoming HTTP requests
Transform Block:
- Add a “Transform” block from Core Blocks
- Place it below the HTTP Endpoint
- This processes the incoming data
Step 5: Connect the Blocks
Section titled “Step 5: Connect the Blocks”- Drag from the HTTP Endpoint’s output socket (bottom)
- Drop onto the Transform block’s input socket (top)
- You’ll see a line showing the connection
Step 6: Configure the Blocks
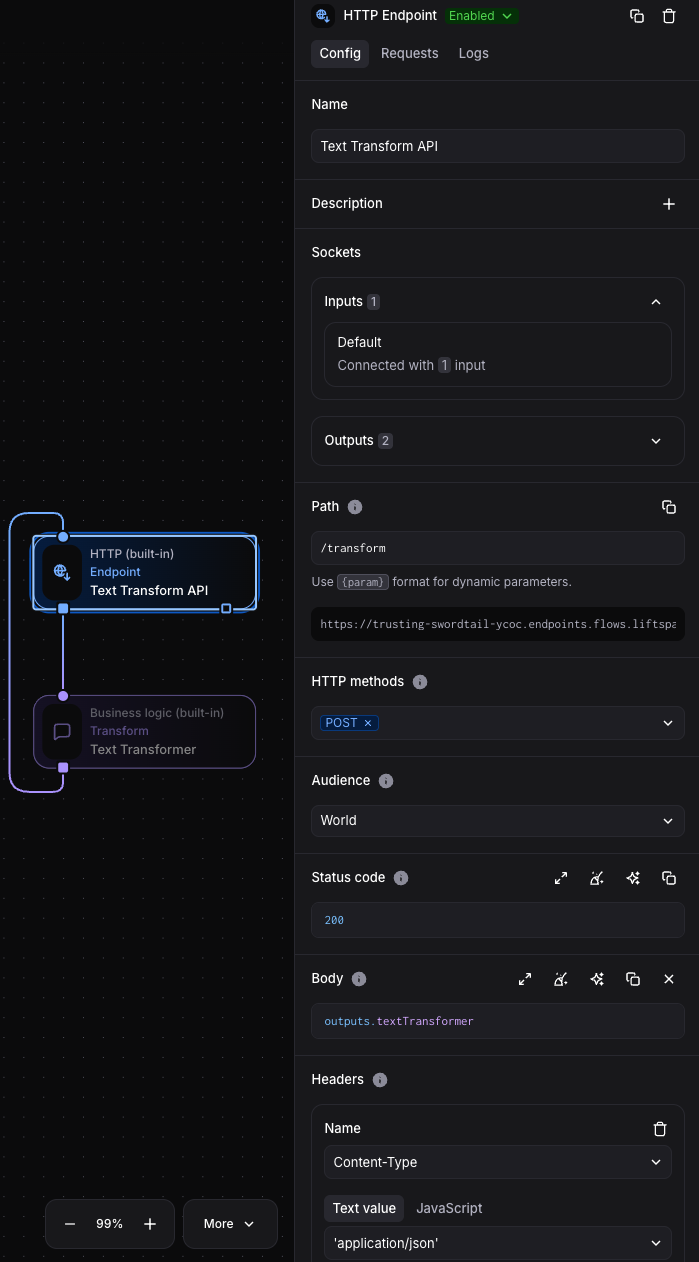
Section titled “Step 6: Configure the Blocks”HTTP Endpoint Configuration:
- Select the block to see settings in the right sidebar
- Name it “Text Transform API”
- Set these values:
- Name: “Text Transform API”
- Path:
/transform - Methods:
POST - Audience: Choose based on your needs
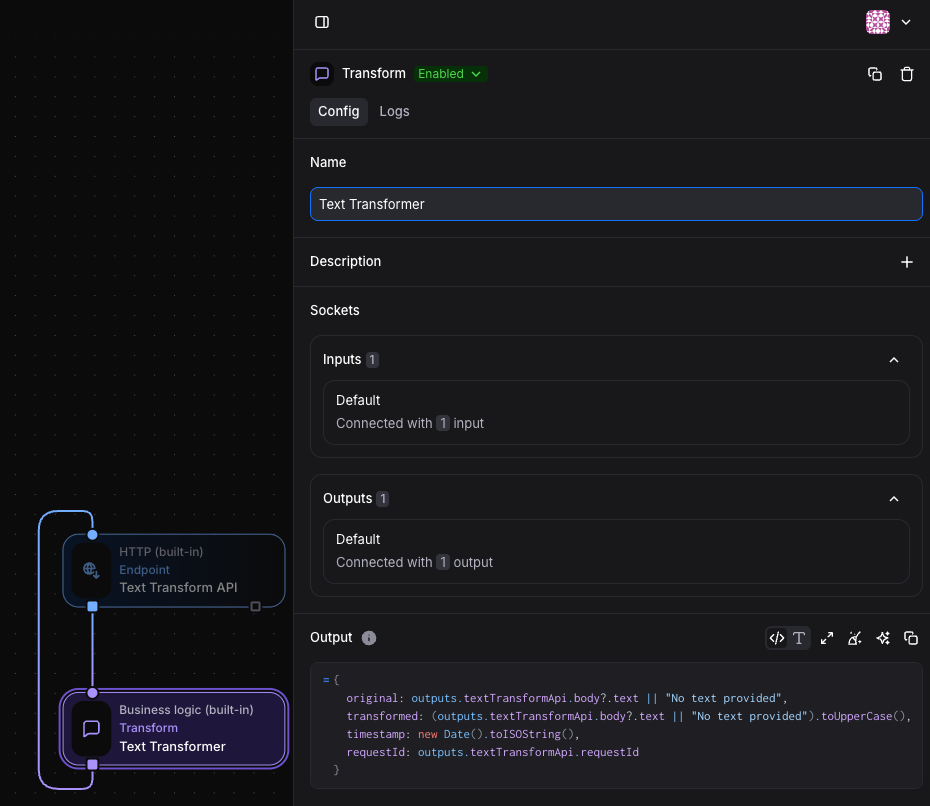
Transform Block Configuration:
- Select the Transform block
- Name it “Text Transformer”
- In the Output field, enter:
{ original: outputs.textTransformApi.body?.text || "No text provided", transformed: (outputs.textTransformApi.body?.text || "No text provided").toUpperCase(), timestamp: new Date().toISOString(), requestId: outputs.textTransformApi.requestId}This expression creates a JSON object that:
original: Captures the input text from the HTTP request body (or defaults to “No text provided” if missing)transformed: Takes the same input text and converts it to uppercasetimestamp: Adds the current date and time in ISO formatrequestId: Includes the request ID from the original HTTP request for tracking
Connect the Response: For the API to respond properly, you need to connect the Transform block’s output back to the HTTP Endpoint’s input:
- Drag from Transform block’s output back to HTTP Endpoint’s input
- Configure the HTTP Endpoint response:
- Header Expressions: Add
Content-Typewith value'application/json' - Response Body:
outputs.textTransformer
- Header Expressions: Add
Step 7: Test Your Flow
Section titled “Step 7: Test Your Flow”- Save the flow
- Copy the webhook URL from the HTTP Endpoint block
- Test with curl:
curl -X POST [your-webhook-url] \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"text": "hello world"}'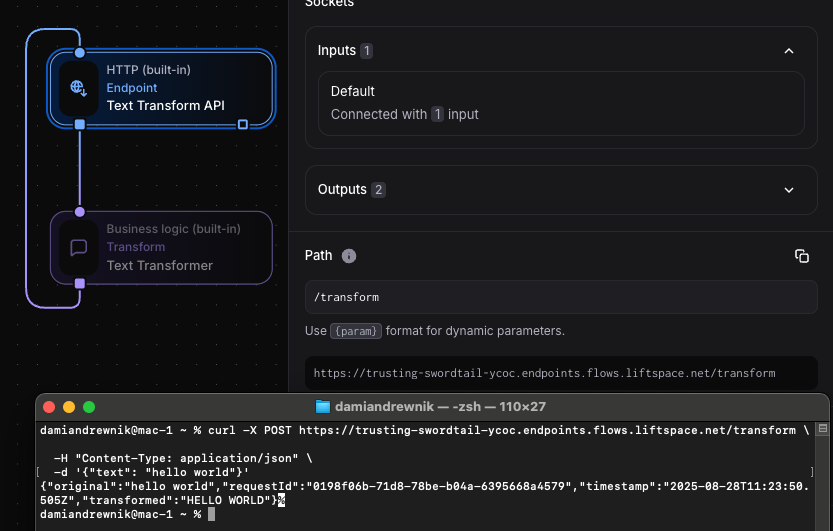
Expected response:
{ "body": { "original": "hello world", "requestId": "0198ea47-3f09-759c-bfad-6b60970c5f93", "timestamp": "2025-08-27T06:46:34.551Z", "transformed": "HELLO WORLD" }, "headers": { "Content-Type": "'application/json'" }, "statusCode": 200}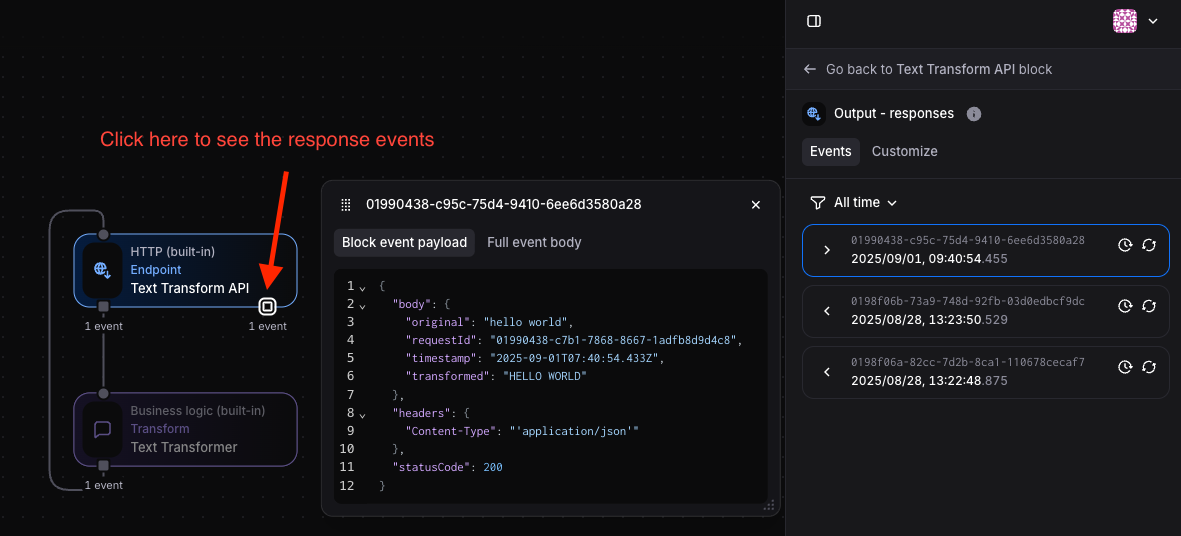
If you need help, click the AI assistant icon in the bottom left of the canvas.
What You Built
Section titled “What You Built”Your flow:
- Accepts POST requests with JSON containing a “text” field
- Transforms text to uppercase
- Returns structured response with original text, transformed text, timestamp, and request ID
- Handles missing text with default message
This demonstrates core Flows concepts:
- Event flow: HTTP requests create events that flow through blocks
- Data accumulation: Each block adds its own output, not discard the others (textTransformApi → textTransformer)
- JavaScript expressions: Dynamic configuration using
outputsvariable
Next Steps
Section titled “Next Steps”Continue with:
- Block Management: Learn how to create, connect, and configure blocks effectively
- Using Event Data: Master JavaScript expressions and data manipulation in your flows
- Core Blocks: Explore HTTP, Time, Business Logic, and Collections blocks for common automation tasks
- Installing Apps: Connect external services like Slack, AWS, or GitHub to your flows
- Flow Organization: Understand projects, permissions, and managing multiple automations