Time Blocks
Time blocks provide timing functionality for your automations - triggering workflows on schedules or adding delays between operations.
Schedule Block
Section titled “Schedule Block”Schedule blocks generate events on a time based schedule without requiring input events. They serve as starting points for flows that run periodically or at specific times. Supported scheduling options include interval based scheduling (every N seconds/minutes/hours) and cron expressions. Timezone configuration ensures schedules execute at the correct local time regardless of infrastructure location.
Configuration
Section titled “Configuration”Frequency-Based Scheduling
Section titled “Frequency-Based Scheduling”For simple interval-based scheduling:
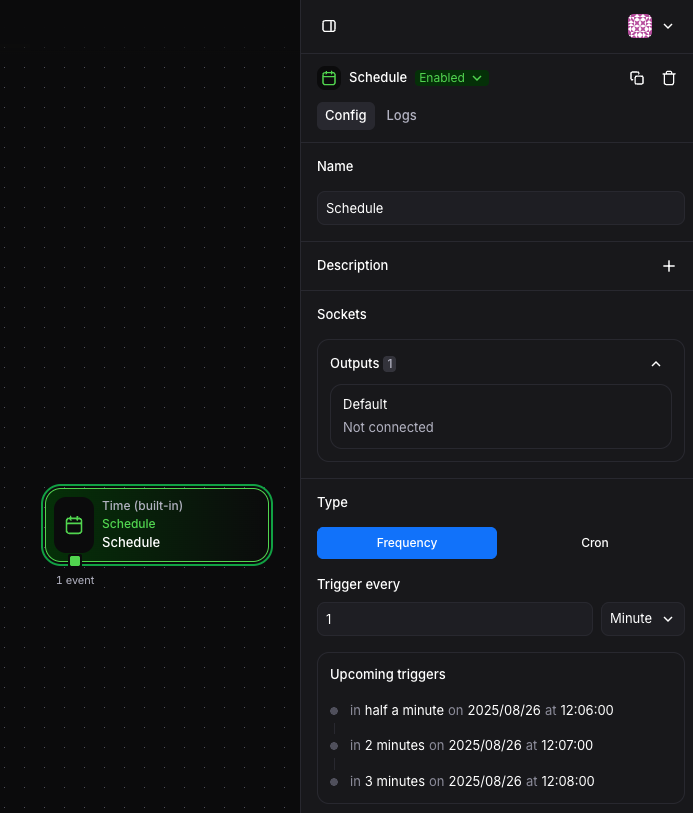
Available units:
- Seconds: High-frequency automations
- Minutes: Regular periodic tasks
- Hours: Less frequent operations
Example: Set to run every 30 minutes by selecting “Minutes” and entering 30.
Cron-Based Scheduling
Section titled “Cron-Based Scheduling”For complex scheduling requirements, use cron expressions:
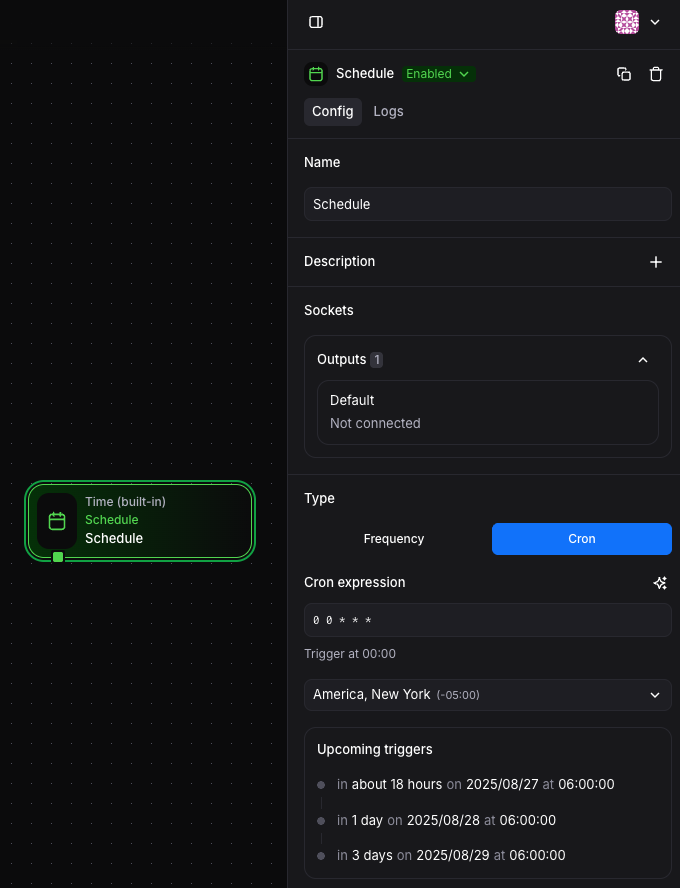
Common patterns:
"0 0 * * *"- Every day at midnight"0 9 * * 1-5"- Every weekday at 9 AM"*/15 * * * *"- Every 15 minutes"0 0 1 * *"- First day of every month at midnight
Sleep Block
Section titled “Sleep Block”Sleep blocks introduce controlled delays into automation flows. They require input events and pause the processing of individual events for a specified duration. The delay can be a fixed number or calculated dynamically based on event data.
Configuration
Section titled “Configuration”The Sleep block uses a field that evaluates to seconds to delay:
Fixed Delays
Section titled “Fixed Delays”30 // Sleep for 30 secondsDynamic Delays
Section titled “Dynamic Delays”outputs.healthCheck.retryAfter || 60Conditional Delays
Section titled “Conditional Delays”outputs.priority === "high" ? 0 : 30This allows you to skip delays for high-priority events while adding delays for normal processing.