Error Block
Overview
Section titled “Overview”The Handle Error block is a special core block in Flows that catches and handles errors from blocks where it has been explicitly assigned as an error handler.
Key Characteristics
Section titled “Key Characteristics”Input: Receives error event data to send back responses or trigger recovery flows
Output: Emits error events containing details about what went wrong
Error Event Structure
Section titled “Error Event Structure”When an error occurs, the Handle Error block emits an event with the following structure (available via the raw variable):
{ error: any, // The actual error object/message operation: string, // What operation was being performed entity: { id: string, // ID of the block/entity that failed entity: string // Type of entity (e.g., "block") }}
// Example Error{ "entity": { "id": "019a11e0-4b5a-771c-a3fe-c9e46586a094", "type": "app_block" }, "error": { "error_handler_id": "019a0b43-da57-7c4b-9309-ad68b2fda96c", "message": "JavaScript error: Error: Search query is required and cannot be empty\n at validateQuery (file:///app/app.js:50:11)\n at Object.onEvent (file:///app/app.js:395:9)" }, "operation": "block.onEvent", "retry": { "was_retried": false }}How It Works
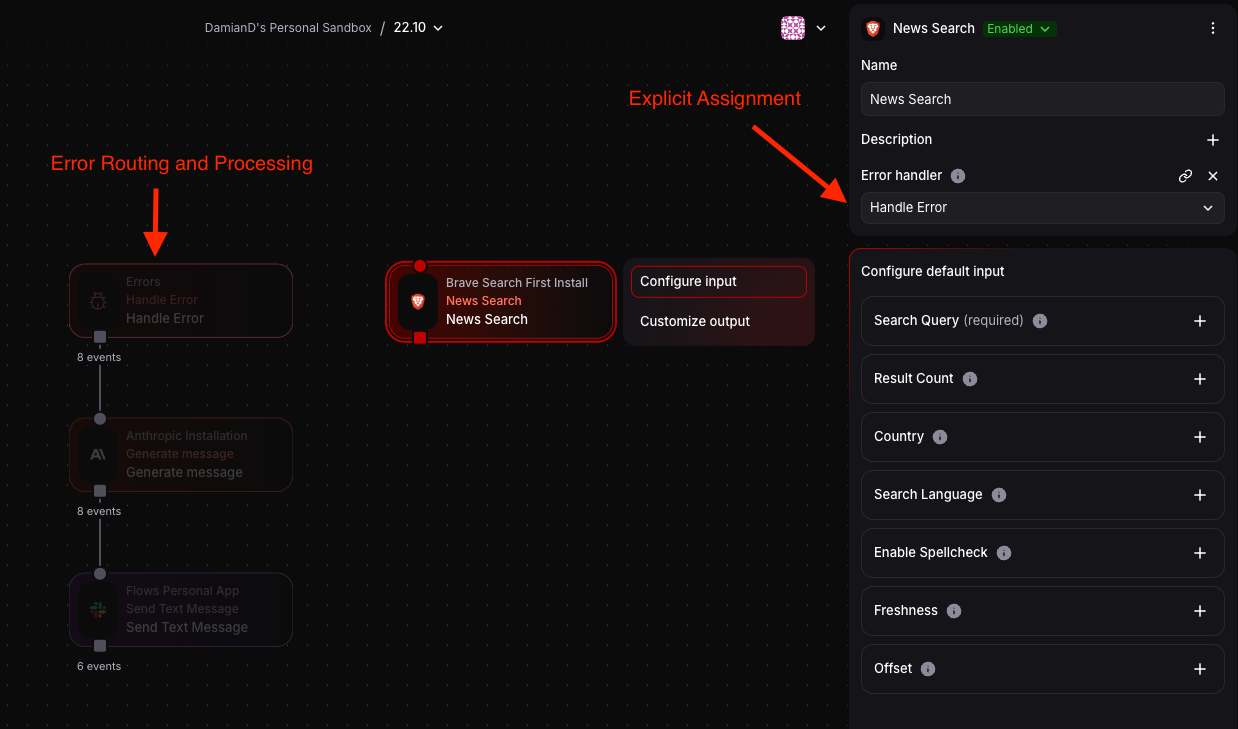
Section titled “How It Works”Explicit Assignment: To catch errors from a specific block, you must assign the Handle Error block as that block’s error handler in the block’s configuration panel. Add a Handle Error block to your flow, then select the block you want to monitor and set its “Error handler” field to your Handle Error block.
Error Routing: When an assigned block throws an error or fails, the Handle Error block receives an error event containing details about the failure.
Error Processing: Connect the Handle Error block’s output to other blocks to process errors (e.g., log to Slack, store in memory, send notifications, implement retry logic).
Multiple Assignments: A single Handle Error block can be assigned to multiple blocks throughout your flow, acting as a centralized error handler.
Common Use Cases
Section titled “Common Use Cases”- Error Logging: Connect to an HTTP Request block to send errors to a logging service
- Notifications: Wire to Slack/email to alert on failures
- Retry Logic: Use with Transform + Memory blocks to implement retry mechanisms
- Graceful Degradation: Route errors to alternative processing paths